FX Oscillograph DCTL
-
Compatibility Davinci Resolve Please check exact version compatibility under the "COMPATIBILITY" tab below
How does it work?
Think about it as a video scope, like Waveform. FX Oscillograph DCTL calculates an average value of pixels and places the graph at the corresponding level. For horizontal graphs, it calculates the average values of the vertical line of pixels, and for vertical graphs, — average of a horizontal line of pixels. Y (White) Graph represents Luminosity, RGB Graph represents each channel. If quantity set to 1, DCTL calculates values of the entire image. If quantity set to 3, for instance, DCTL divides the image into 3 equal parts and each graph displays values of these parts.
Try out the free demo version. In the demo, you will have 40% of the frame staying without DCTL.

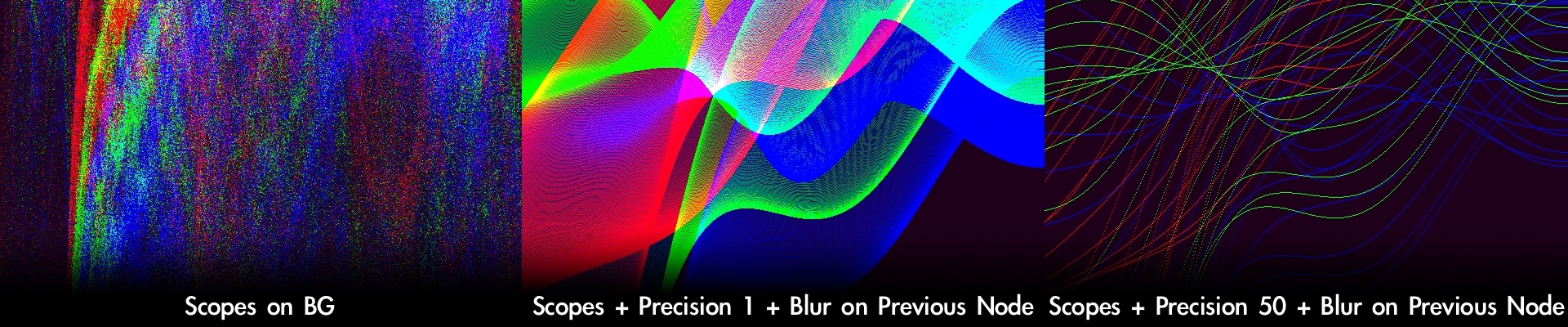
Add Luminance or RGB Waveform on the Background
Combine with a blur on the previous node to change the waveform's appearance. Use layer nodes in Add composite mode to combine blurred waveform on the background and sharp graphs on the foreground.
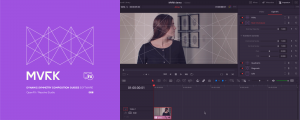
Quick User Guide
On the Edit or Color page, open Effects tab and apply DCTL on your clip or node. Select NP FX Oscillograph from the DCTL List.
Use Quantity slider to add more graphs. Use Background sliders to change background transparency and color. If you want graphs colored in actual average values, use checkboxes Actual Values.
If your workstation has low performance, do not use low Precision values in pair with low Quantity values.
Since the DCTL uses input image to build the graph, you can also change the graph by adjusting the image on the previous nodes.
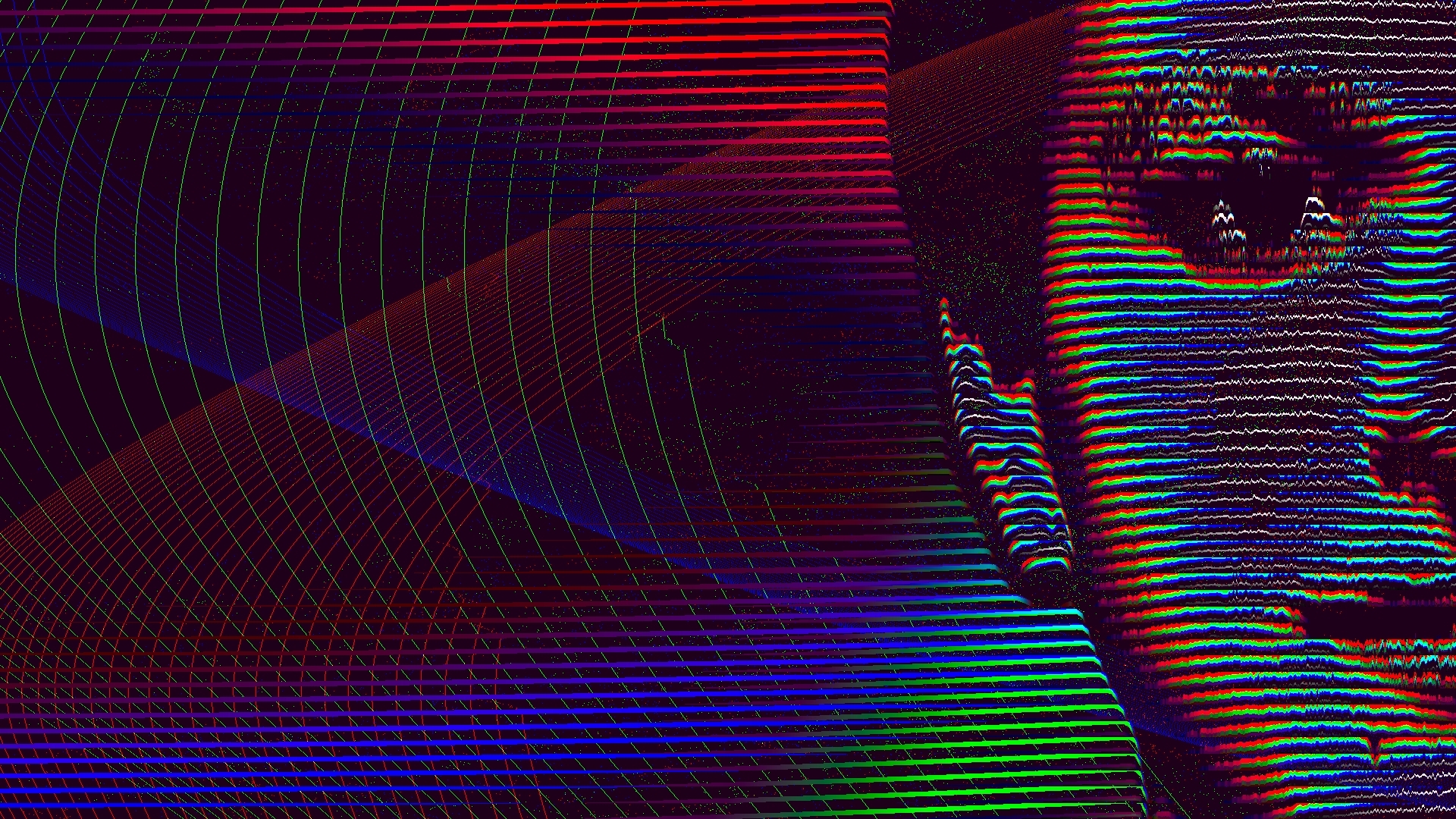
Complete User Manual
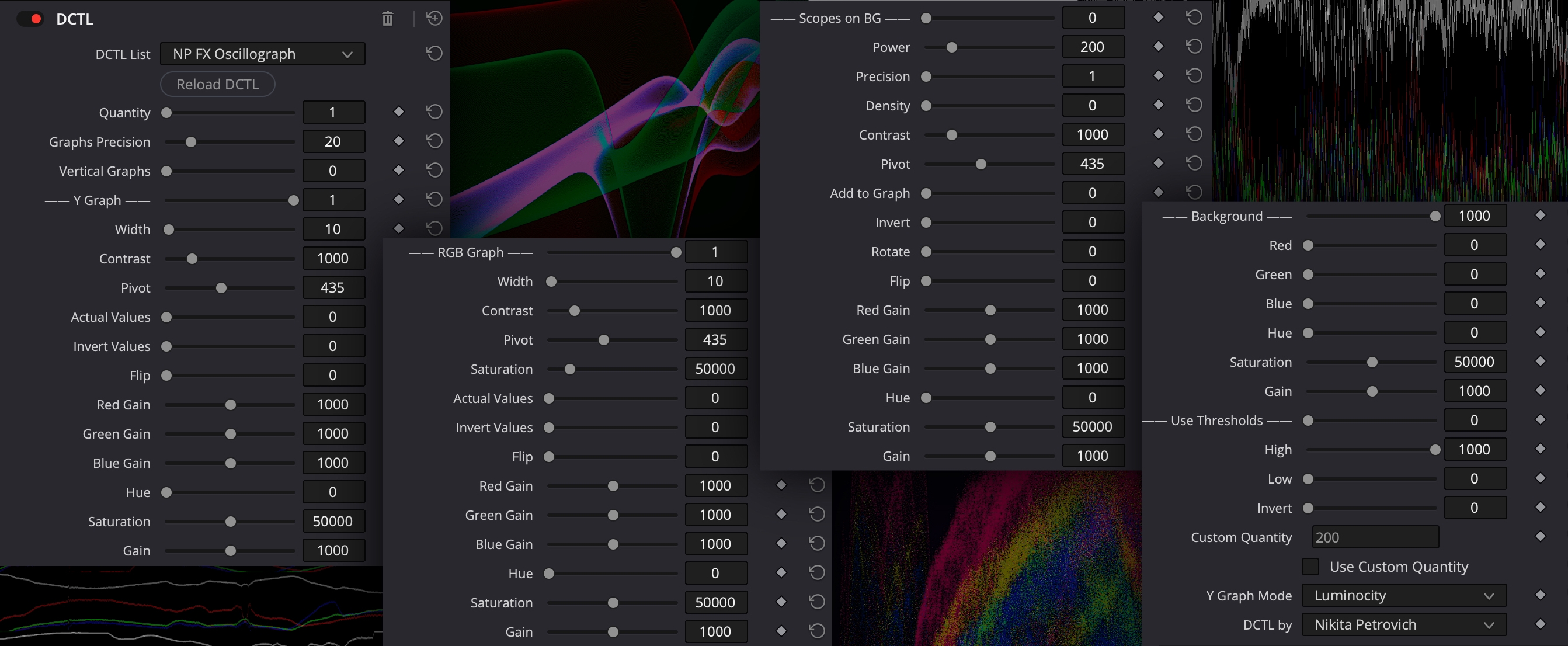
Parameters marked with '*' sign in the user manual were multiplied by 1000 (Hue - by 10) inside the UI. This is done to arrange sliders in a user-friendly order, since DCTLs have limitations in UI flexibility.
- Quantity - changes the amount of rows with graphs. More Quantity - less Precision number can be used without fps drops.
- Graphs Precision - controlling the amount of pixels to calculate average values. Less is better. 1 - uses each pixel, 3 - uses each third pixel, 12 - uses each 12th pixel and so on. Use Precision to optimize real-time playback. More Quantity - less Precision number can be used without fps drops.
- Vertical Graphs - changes graphs to vertical and graphs represent average values of horizontal lines of pixels.
- — Y/RGB Graph — - disables/enables corresponding graphs.
- *Width - makes lines bolder.
- *Contrast - makes graph steeper with sharper peaks by changing contrast of input image and calculates average for changed values. Contrast is linear and doesn't affect the visible image under the graph.
- *Pivot - changes the pivot point of applied contrast.
- *Saturation - moves RGB lines from each other by changing saturation of input image and calculates average for changed values. Saturation is standard (based on Luminance) and doesn't affect the visible image under the graph.
- Actual Values - uses actual average pixels' values to color corresponding graphs.
- Invert Values - inverts colors of corresponding graphs.
- Flip - flips corresponding graphs.
- *Red, Green, Blue Gain - gain corresponding color channels of output image.
- *Hue - changes hue of output image.
- *Saturation - changes saturation of output image.
- *Gain - applies gain to output image.
- — Scopes on BG — - adds waveform behind graphs: 1 - Luminance Waveform, 2 - RGB Waveform. Do not use it for color critical work, artistic use only.
- *Power - changes waveform visibility
- Precision - controlling the amount of pixels to analyze image. Less is better. 1 - uses each pixel, 3 - uses each third pixel, 12 - uses each 12th pixel and so on. Use Precision to optimize real-time playback.
- Density - makes waveform ‘dots’ longer. Useful when the waveform looks like lines and you want to make these lines bolder.
- *Contrast - adjusts waveform appearance by changing contrast of input image. Contrast is linear and doesn't affect the image under the waveform.
- *Pivot - changes the pivot point of applied contrast.
- Add to Graph - changes composite mode of waveform to 'Add', so it will be mixed with graphs.
- Invert - inverts color of waveform 'dots'. Doesn't invert completely black pixels.
- Rotate - changes waveform to horizontal and waveform analyzes horizontal lines of pixels.
- Flip - flips waveform.
- *Red, Green, Blue Gain - gain corresponding color channels of output image.
- *Hue - changes hue of output image.
- *Saturation - changes saturation of output image.
- *Gain - applies gain to output image.
- *— Background — - revealing the input image under the graph. 0 - input image is visible. 1000 - input image is filled with color and Scopes.
- *Red, Green, and Blue Background - changes the filling color of the background.
- *Hue - changes hue of output image.
- *Saturation - changes saturation of output image.
- *Gain - applies gain to output image.
- *High and Low Threshold - revealing the input image outside the defined range. Disabled by default. Use the slider '— Use Thresholds —' to enable. To invert the range, use the slider 'Invert'.
- Custom Quantity - user defined Quantity. To enable it, use the checkbox 'Use Custom Quantity'.
- Y Graph Mode:
- Luminance - graph colored in luminance values.
- Maximum - graph colored in the channel with maximum average values of corresponding lines of pixels.
- Minimum - graph colored in the channel with minimum average values of corresponding lines of pixels.
PLEASE NOTE: DCTLs work only in the Studio version of DaVinci Resolve
| Davinci Resolve | 19, 18, 17, 16 |
|---|
0.3.0 (Current version) - Aug 18, 2024
- Adjust R, G, and B Gain, Hue, Saturation, and Gain of each element - Y Graph, RGB Graph, Scopes, and Background.
- Density - makes waveform ‘dots’ longer. Useful when the waveform looks like lines and you want to make these lines bolder.
CHANGED:
Background color sliders now have range from 0 to 1000.
0.2.0 - Aug 9, 2024
— Scopes on BG — - adds waveform behind graphs: 1 - Luminance Waveform, 2 - RGB Waveform. Do not use it for color critical work, artistic use only.
- Power - changes waveform visibility
- Precision - controlling the amount of pixels to analyze image. Less is better. 1 - uses each pixel, 3 - uses each third pixel, 12 - uses each 12th pixel and so on. Use Precision to optimize real-time playback.
- Contrast - adjusts waveform appearance by changing contrast of the input image. Contrast is linear and doesn't affect the image under the waveform.
- Pivot - changes the pivot point of applied contrast.
- Add to Graph - changes composite mode of waveform to 'Add', so it will be mixed with graphs.
- Invert - inverts color of waveform 'dots'. Doesn't invert completely black pixels.
- Rotate - changes waveform to horizontal and waveform analyzes horizontal lines of pixels.
- Flip - flips waveform.
UI CHANGES:
Parameters with floating point were multiplied by 1000 and Checkboxes were changed to sliders with two values: 0 and 1. This is done to arrange parameters in a user-friendly order, since DCTLs have limitations in UI flexibility.
FIXED:
Background color sliders now have correct 8-bit precision. They had little offset before.
 Adding to cart...
Adding to cart...